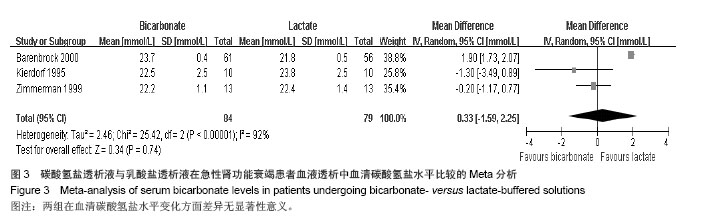
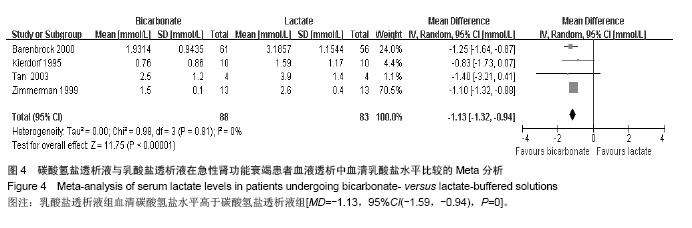
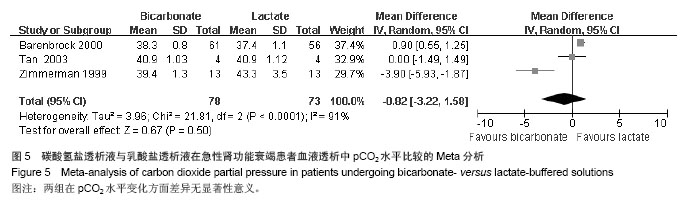
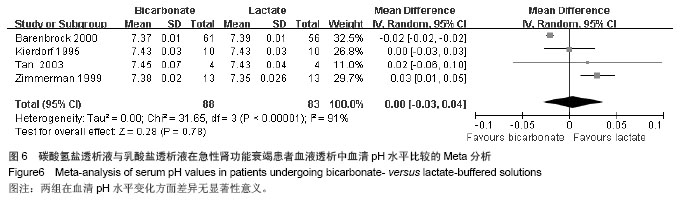
| [1]Palipoch S.A review of oxidative stress in acute kidney injury: protective role of medicinal plants-derived antioxidants.Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med. 2013;10(4):88-93.
[2]Chawla LS,Kimmel PL.Acute kidney injury and chronic kidney disease: an integrated clinical syndrome. Kidney Int. 2012; 82(5):516-524.
[3]陈惠萍,曾彩虹,黎磊石,等.急性肾功能衰竭的病理类型分析[J].中国危重病急救医学,2000,12(4):228-231.
[4]Bellomo R,Kellum JA,Ronco C.Acute kidney injury.Lancet. 2012;380(9843):756-766.
[5]Davies H,Leslie G.Acute kidney injury and the critically ill patient. Dimens Crit Care Nurs.2012;31(3):135-152.
[6]Fleming GM.Renal replacement therapy review: past, present and future. Organogenesis.2011;7(1):2-12.
[7]Guest S.Hypoalbuminemia in peritoneal dialysis patients.Adv Perit Dial. 2013;29:55-60.
[8]Basile C,Lomonte C.Dialysis: A step towards optimal dialysate bicarbonate concentration. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2013; 9(10):565-566.
[9]Mercadal L,Petitclerc T.Technical advances in haemodialysis. Nephrol Ther. 2009;5(2):109-113.
[10]Daimon S,Dan K,Kawano M.Comparison of acetate-free citrate hemodialysis and bicarbonate hemodialysis regarding the effect of intra-dialysis hypotension and post-dialysis malaise.Ther Apher Dial.2011;15(5):460-465.
[11]Kuragano T,Kida A,Furuta M,et al.Effects of acetate-free citrate-containing dialysate on metabolic acidosis, anemia, and malnutrition in hemodialysis patients.Artif Organs. 2012; 36(3):282-290.
[12]Mehta RL,Kellum JA,Shah SV,et al.Acute Kidney Injury Network: report of an initiative to improve outcomes in acute kidney injury.Crit Care.2007;11(2):R31.
[13]Iglesias J,Lieberthal W,Johnson RJ,et al.Clinical evaluation of acute renal failure. Comprehensive Clinical Nephrology. 2000: 1-15.
[14]Higgins JPT,Green S.Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions, Version 5.0.2. The Cochrane Collaboration 2008.Available at: http://www.cochrane-handbook. rg.
[15]Zimmerman D,Cotman P,Ting R,et al.Continuous venovenous haemodialysis with a novel bicarbonate dialysis solution: prospective cross-over comparison with a lactate buffered solution.Nephrol Dial Transplant.1999;14(10): 2387-2391.
[16]Tan HK,Uchino S,Bellomo R.The acid-base effects of continuous hemofiltration with lactate or bicarbonate buffered replacement fluids.Int J Artif Organs.2003;26(6):477-483.
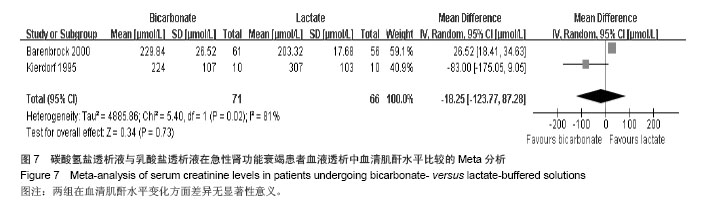
[17]Kierdorf H, Leue C,Heintz B,et al.Continuous venovenous hemofiltration in acute renal failure: is a bicarbonate- or lactate-buffered substitution better? Contrib Nephrol. 1995; 116:38-47.
[18]Barenbrock MH,Hausberg M,Matzkies F,et al.Effects of bicarbonate and lactate-buffered replacement fluids on cardiovascular outcome in CVVH patients. Kidney Int. 2000; 58(4):1751-1757.
[19]Macedo E,Mehta RL.Timing of dialysis initiation in acute kidney injury and acute-on-chronic renal failure.Semin Dial. 2013;26(6):675-681.
[20]Macedo E, Mehta RL.When should renal replacement therapy be initiated for acute kidney injury? Semin Dial. 2011;24(2): 132-137.
[21]Rahman S,Rubinstein S,Singh J,et al.Early use of hemodialysis for active rewarming in severe hypothermia: a case report and review of literature.Ren Fail. 2012;34(6):784-788.
[22]Caluwé R,Vanholder R,Dhondt A. Hemodialysis as a treatment of severe accidental hypothermia.Artif Organs. 2010; 34(3):237-239.
[23]García-López E,Lindholm B,Davies S.An update on peritoneal dialysis solutions.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2012;8(4):224-233.
[24]Bersenas AM.A clinical review of peritoneal dialysis.J Vet Emerg Crit Care. 2011;21(6):605-617.
[25]Negi S,Koreeda D,Shigematsu T.Continuous renal replacement therapy in acute kidney injury.Nihon Jinzo Gakkai Shi.2013;55(4):529-533.
[26]Wu MY,Hsu YH,Bai CH,et al.Regional citrate versus heparin anticoagulation for continuous renal replacement therapy: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Am J Kidney Dis.2012;59(6):810-818.
[27]Tillman J.Heparin versus citrate for anticoagulation in critically ill patients treated with continuous renal replacement therapy. Nurs Crit Care. 2009;14(4):191-199.
[28]Vitale C,Bagnis C,Marangella M.Computer program to prescribe acetate-free biofiltration as a continuous renal replacement therapy: theoretical description and in vivo validation.J Nephrol.2006;19(2):168-175.
[29]Zobel G,Rödl S,Urlesberger B,et al.Continuous renal replacement therapy in critically ill patients.Kidney Int Suppl. 1998;66:S169-173.
[30]Perazella MA,Cruz DN.Ringer's lactate: an inexpensive and effective dialysate for continuous renal replacement therapy. Am J Kidney Dis.1999;33(3):614-615.
[31]Adhikari NK,Van Wert R,Scales DC,et al.High-dose renal replacement therapy for acute kidney injury: Systematic review and meta-analysis-addendum.Crit Care Med. 2010; 38(12):2424-2425.
[32]Allegretti AS,Steele DJ,David-Kasdan JA,et al.Continuous renal replacement therapy outcomes in acute kidney injury and end-stage renal disease: a cohort study.Crit Care. 2013; 17(3):R109.
[33]Parienti JJ,Dugué AE,Daurel C,et al.Continuous renal replacement therapy may increase the risk of catheter infection.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol.2010;5(8):1489-1496.
[34]Kawarazaki H,Uchino S,Tokuhira N,et al.Who may not benefit from continuous renal replacement therapy in acute kidney injury? Hemodial Int.2013;17(4):624-632.
[35]Karnad V,Thakar B. Continuous renal replacement therapy may aid recovery after cardiac arrest. Resuscitation. 2006; 68(3):417-419. |